Major Types of Dietary Antioxidants

Many types of antioxidants are present in food, especially in fruits and vegetables. They are classified in groups according to their chemical structures. Examples are listed below. This list is by no means to be comprehensive.
Vitamin-based antioxidants
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) – It is found in citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, bell peppers, leafy greens, and animal liver. It plays an important role in the synthesis of collagen, a protein that is required for strengthening skin, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels. A severe form of vitamin C deficiency is known as scurvy. Vitamin C has a protective effect against stroke. However, its beneficial effects against coronary heart disease and cancer are still controversial after 33 years of studies.
Vitamin E (tocopherols & tocotrienols) – Existed in eight different chemical forms, vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables. It protects cell membranes from oxidation. Its main role is to act as an antioxidant, scavenging free radicals that can damage cells. Vitamin E has many health benefits, including lowering of cancer risk, improved eye health, boosting immune system, guarding against blood clots, and brightening skin.
Polyphenols
Flavonoids
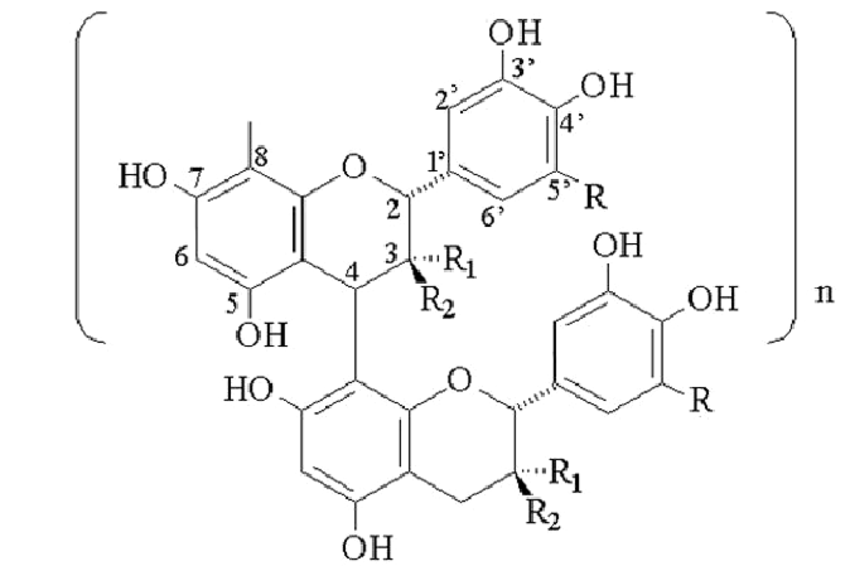
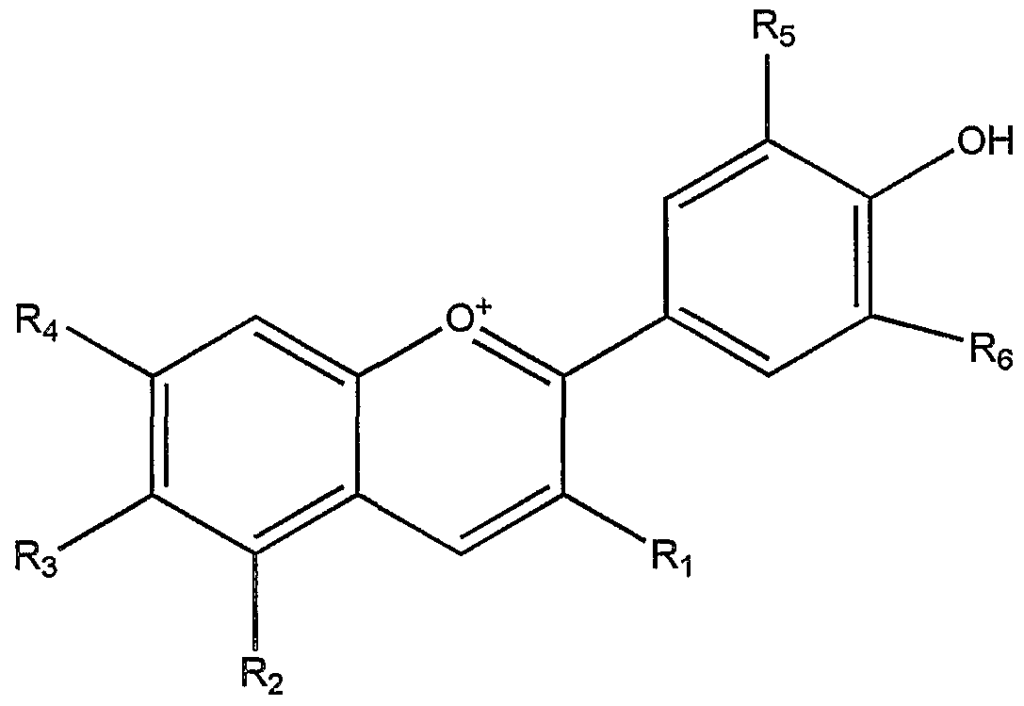
Flavonoids are a large group of plant-derived polyphenolic compounds, and are classified into seven major subtypes based on their chemical structure: flavones, flavonols, flavanones, flavan-3-ols (also known as flavanols), anthocyanins, isoflavones and catechins. Here are some well-known examples.
Quercetin – It is a flavonol found in citrus fruits, apple, onion, tea and many berries. It inhibits growth of cancer cells, especially to cancers of blood, brain, lung, uterine, skin and salivary gland. It also helps protect against cardiovascular diseases. In addition, it has antihistamine and anti-inflammatory properties, and may help reduce symptoms of allergies.
Luteolin – It is a flavone found in fruits and vegetables such as celery, broccoli, cabbage, green pepper, and carrot, and has anti-inflammation, anti-allergy and anti-cancer activities. It inhibits proliferation of some cancer cells, regulates mast cell-mediated inflammatory diseases and allergy, and promotes cardiovascular health. Furthermore, it has selective toxicity against cancerous cells, but not normal cells, making it a good supplement for cancer prevention.
Genistein – It is an isoflavone found in high abundance in soybean and soy products. It has antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammation and anti-diabetic activities. Structurally, it is similar to estrogen, so it is a phytoestrogen. It can bind to estrogen receptors and modulate their activities. Therefore, it can increase growth rate of some estrogen receptor-expressing breast cancers. However, it can suppress growth of other cancers such as prostate and ovarian cancers. It inhibits tumor metastasis by suppressing angiogenesis (blood vessel formation) and tumor invasion. It also activates tumor suppressor genes and affects cancer cell survival. On the other hand, it has anti-inflammatory effect, and is a promising agent for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Its ability to modulate vascular inflammation helps to prevent atherosclerosis. It is also anti-diabetic, as it has direct effect on beta-cell proliferation.
Oligomeric Proanthocyanidins (OPCs) – OPCs are polymers of flavan-3-ols, such as catechin and epicatechin. They are found in fruits, chocolate, wine and tea, and are much powerful than vitamins C and E. Commercial supplements are generally extracted from maritime pine bark and grape seed. They exhibit selective cytotoxicity towards human cancer, and reduce risk of coronary heart disease via inhibition of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation and relaxation of blood vessels. They improve diabetic complications, and have antibacterial activity. Furthermore, they also strengthen collagen and elastin, the two proteins in connective tissues that support blood vessels. Therefore, they are beneficial to people with bleeding hemorrhoid.
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) – It is a type of catechin found mainly in green tea. People who consume green tea have lower risk of developing various cancers. Animal studies showed that EGCG protected against development of cancers of skin, lung, mammary gland, and gastrointestinal tract. Green tea extracts were shown to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) of various cancer cells. EGCG inhibits tumor invasion and angiogenesis (blood vessel formation), which are required for tumor metastasis. It also inhibits dihydrotestosterone (DHT) activity, which is associated with the enlargement of prostate gland.
Phenolic Acids
Phenolic acids are a diverse group of naturally occurring plant compounds characterized by an aromatic ring bearing one or more hydroxyl groups and a carboxylic acid group. They are found in various plant parts and are abundant in fruits, vegetables, grains, and beverages. Research suggests that dietary intake of phenolic acids may be associated with reduced risks of certain diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers.
Gallic acid – It is a naturally occurring phenolic compound found in many plants, fruits, and beverages. It is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties.
Ellagic acid – Itis a naturally occurring polyphenol found in various fruits and vegetables, notably berries, pomegranates, and walnuts. It is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative properties, potentially offering benefits for skin health, metabolic health, and even cancer prevention.
Stilbenes
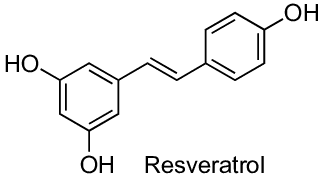
Stilbenes are a class of natural phenolic compounds found in plants, characterized by a 1,2-diphenylethylene nucleus. They are known for their various biological activities, including anticancer, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. Resveratrol is a well-known example of a stilbene.
Resveratrol – It is found in skin of dark grape, red wine, a variety of berries and peanut. It has been shown to activate endogenous antioxidant enzymes. In animal studies, it has been shown to inhibit growth of several human cancer types and to sensitize cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Furthermore, it has also beneficial effects in animal studies of hypertension, arteriosclerosis, stroke and other cardiovascular diseases. It improves glycemic control and decreases insulin resistance in type-2 diabetes. Although the animal studies on resveratrol are very promising, clinical studies are still limited and inconsistent. The clinical data of the optimal dose and long-term studies are still lacking. The main problem with natural resveratrol is its fast metabolization in human body.
Lignans
Lignans are a group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. They are known for their potential health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. Lignans are also precursors to phytoestrogens, and some evidence suggests they may play a role in preventing cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
Nonflavonoid phenolics
Curcumin – It belongs to a polyphenolic subgroup known as curcuminoids, and is found in tumeric (a component of curry). It has antioxidant, antibacterial and anticancer properties. It inhibits proliferation of various cancer cells in culture, and inhibits growth of human prostate cancer in animal studies. Furthermore, it also used for diabetes prevention and treatment. However, it is not effective for treatment of dementia, due to its poor absorption and rapid metabolization in intestine and liver.
Carotenoids
Beta-Carotenes – Carotenes are the photosynthetic pigments that give orange color in fruits and vegetables. They exist in five forms, among them beta-carotene is the most abundant. Beta-carotene is found in yellow, orange or red fruits and vegetables, and dark leafy greens. It can be converted to vitamin A in human body. Clinical studies showed that beta-carotene has no protective effects on the development of lung cancer. In fact, high doses of beta-carotene may increase the risk of lung cancer in smokers. High dose of beta-carotene supplement is not recommended.
Lycopene – It is the bright red carotenoid pigment found in tomato, watermelon, papaya, and carrot. Consumption of tomatoes has been linked to lower risk of prostate cancer. Laboratory studies using prostate cancer cells showed that lycopene can inhibit cancer cell growth, and it is nontoxic to normal cells. However, results of studies with animal models are inconsistent. Confirmation of the laboratory studies by clinical trials is still lacking. The use of lycopene in the prevention or treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia has not been confirmed to be effective.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin – They are the carotenoid pigments that give the yellow or orange color in fruits and vegetables. They are found in green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale), yellow or orange fruits and vegetables (corn, pumpkin, orange) and egg yolk. They act as scavengers of free radicals and protect the macula from damage by blue light. Clinical studies have established their role in human eye health, preventing and reducing cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
Astaxanthin – It is the red-orange carotenoid pigment found in microalgae, krill, salmon, shrimp and lobster. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and is more potent than vitamin E and beta-carotene. It reduces oxidative stress and inflammation that are associated with many degenerative diseases. The cardiovascular protective effects have been demonstrated in animal studies but have not yet been confirmed in clinical studies. It has been shown to prevent neurodegeneration, as well as cancer development. Together with lutein and zeaxanthin, it improves vision.
Minerals
Selenium – It is an essential trace mineral and is incorporated into some selenoproteins in the forms of selenocysteine or selenomethionine. Selenium is found in seafood, meat, eggs and whole grains. Although laboratory studies on the effects of selenium in cancer prevention are promising, clinical studies showed that selenium supplement is not effective for cancer prevention. It may increase risk of certain cancer such as prostate cancer. Limited clinical studies also showed no beneficial effects on cardiovascular diseases. Selenium supplement is not recommended for prevention of cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Other antioxidant compounds
Glutathione – It is a powerful antioxidant produced naturally in the body. It’s composed of three amino acids and plays a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals and other harmful substances. Glutathione is often called the “master antioxidant” because it helps recycle other antioxidants like vitamins C and E. Foods high in glutathione include asparagus, avocados, broccoli, spinach, and foods rich in sulfur (like garlic and onions). Cruciferous vegetables (like kale and Brussels sprouts) also contribute to glutathione production due to their sulfur content.
Melatonin – It is a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. It also acts as a potent antioxidant through both direct and indirect mechanisms. It directly scavenges free radicals and also enhances the body’s natural antioxidant defenses by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes. This dual action makes melatonin a valuable molecule in protecting against oxidative stress and related damage. Several foods naturally contain melatonin, good sources include nuts, fish, eggs, milk, tart cherries, mushrooms, and certain fruits like grapes and bananas.
Which antioxidant is good for me?
For the information of the best antioxidant supplement, please go to this page. There are other antioxidant supplements for special needs. For details, please go to this page.